Importing Binary Records
Binary files excel in data storage and transfer efficiency while maintaining data structure and format. Theirunreadable format provides natural security benefits, making binary files an optimal choice for handling large-scale data that requires both performance and protection.
This page covers the processes of exporting and importing binary files in DolphinDB.
Exporting Data to Binary Files
To prepare a binary file for subsequent importing, we'll start by exporting a
DolphinDB in-memory table to a binary file using the writeRecord
function. Note that writeRecord only supports binary files with
fixed-length rows and consistent data types. It cannot handle strings.
Given an in-memory table:
id = [1,2,3,4,5]
date = take(20240310,5)
time = take(130000000,5)
value = rand(10,5)\5
tmp = table(id,date,time,value)Save the table to an existing binary file demo1.bin using
writeRecord:
dataFilePath = "./binaryFile/demo1.bin"
f = file(dataFilePath,"w")
writeRecord(handle = f, object = tmp)
f.close()The binary file must be created before calling writeRecord.
Loading to Memory
DolphinDB offers two functions for binary file import:
readRecord!: Converts binary files to DolphinDB objects, without supporting strings.loadRecord: Imports binary files with fixed-length rows into memory, supporting strings.
Using readRecord! requires pre-defining a table schema to store the
imported data.
tmpTB = table(1:0,["id","date","time","value"],[INT,INT,INT,DOUBLE])Before importing the data, you must open the binary file in readable mode using the
file function:
dataFilePath = "./binaryFile/demo1.bin"
f = file(dataFilePath) Then, use readRecord! to import the data to in-memory table tmpTB,
and close the file:
readRecord!(f, tmpTB)
f.close()
tmpTB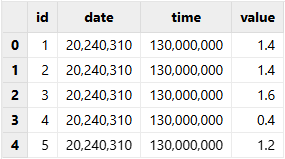
The dates in demo1.bin are stored using INT data type. When reading the binary file, directly converting INT-stored dates and time values to temporal types will produce incorrect results.
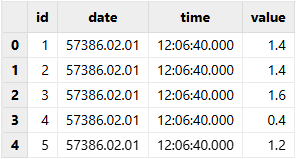
tmpTB1 = table(1:0,["id","date","time","value"],[INT,DATE,TIME,DOUBLE])
f = file(dataFilePath)
readRecord!(f, tmpTB1)
f.close()
tmpTB1Output:
To handle this, convert the INT-type time columns to strings first, then use
temporalParse to transform them into proper date and time
formats.
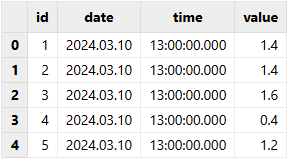
replaceColumn!(table = tmpTB, colName="date",
newCol=tmpTB.date.format("00000000").temporalParse("yyyyMMdd"))
replaceColumn!(table = tmpTB, colName="time",
newCol=tmpTB.time.format("000000000").temporalParse("HHmmssSSS"))
tmpTBOutput:
The loadRecord function imports binary files similarly to text files
- just specify the file path and schema. Since binary files don't include type
information, you must explicitly define the schema as a tuple containing
column names and data types. For string columns, include the string length.
dataFilePath = "./binaryFile/demo1.bin"
schema = [("id",INT),("date",INT),("time",INT),("value",DOUBLE)]
loadRecord(dataFilePath, schema) 