fminLBFGSB
Syntax
fminLBFGSB(func, X0, [fprime], [bounds], [m=10], [factr=1e7], [pgtol=1e-5],
[epsilon=1e-8], [maxIter=15000], [maxFun=15000], [maxLS=20])
Parameters
func is the function to minimize. The return value of the function must be numeric type.
X0 is a numeric scalar or vector indicating the initial guess.
fprime (optional) is the gradient of func. If not provided, then
func returns the function value and the gradient (f, g = func(x,
*args)).
bounds (optional) is a numeric matrix indicating the bounds on parameters of
X0. The matrix must be in the shape of (N,2), where
N=size(X0). The two elements of each row defines the bounds (min,
max) on that parameter. float("inf") can be specified for no bound
in that direction.
m (optional) is a positive integer indicating the maximum number of variable metric corrections used to define the limited memory matrix. The default value is 10.
factr (optional) is a positive number to stop the iteration when 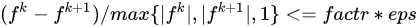 , where
eps is the machine precision. Typical values for factr are: 1e12
for low accuracy; 1e7 (default) for moderate accuracy; 10.0 for extremely high
accuracy.
, where
eps is the machine precision. Typical values for factr are: 1e12
for low accuracy; 1e7 (default) for moderate accuracy; 10.0 for extremely high
accuracy.
pgtol (optional) is a positive number to stop the iteration when 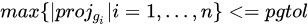 , where proj g_i
is the i-th component of the projected gradient. The default value is 1e-5.
, where proj g_i
is the i-th component of the projected gradient. The default value is 1e-5.
epsilon (optional) is a positive number indicating the step size used for numerically calculating the gradient. The default value is 1e-8.
maxIter (optional) is a non-negative integer indicating the maximum number of iterations. The default value is 15000.
maxFun (optional) is a non-negative integer indicating the maximum number of function evaluations. The default value is 15000.
maxLS (optional) is a non-negative integer indicating the maximum number of line search steps (per iteration). The default value is 20.
Details
Minimize a function func using the L-BFGS-B algorithm.
Return value: A dictionary with the following members:
-
xopt: A floating-point vector indicating the parameters of the minimum.
-
fopt: A floating-point scalar indicating the value of func at the minimum, i.e.,
fopt=func(xopt). -
gopt: A floating-point vector indicating the gradient at the minimum, i.e.,
gopt=func'(xopt). -
iterations: The number of iterations.
-
fcalls: The number of function calls made.
-
warnFlag: An integer, which can be
-
0: Minimization performed.
-
1: Maximum number of evaluations/iterations exceeded.
-
2: Stopped for other reasons.
-
Examples
X = double(0..9)
M = 2
B = 3
Y = double(M * X + B)
def fun(params, x, y) {
m = params[0]
b = params[1]
y_model = m*x + b
error = sum(square(y - y_model))
return error
}
initial_values = [0.0, 1.0]
fminLBFGSB(fun{,X,Y}, initial_values)Output:
fcalls->27
warnFlag->0
xopt->[1.999999985435,3.000000060585]
gopt->[8.05E-10,8.84E-10]
fopt->0E-12
iterations->6