Cumulative Moving TopN Functions (cumTopN functions)
DolphinDB provides cumulative moving topN (cumTopN) functions to perform calculations on the top N elements in a cumulative sliding window.
Introduction
Syntax templates for cumTopN functions:
cumTopN(X, S, top, [ascending=true], [tiesMethod]='latest')
cumTopN(X, Y, S, top, [ascending=true], [tiesMethod='latest'])Parameters:
X (Y) is a numeric vector or matrix.
S is a numeric/temporal vector or matrix, based on which X are sorted. Null values in S are ignored.
top is an integer, indicating the first top elements of X after sorted based on S.
ascending (optional) is a Boolean value indicating whether to sort S in ascending order. It is an optional parameter and the default value is true.
-
'oldest': select elements starting from the earliest entry into the window;
-
'latest': select elements starting from the latest entry into the window;
-
'all': select all elements.
List of Functions
cumTopN(X, S, top, [ascending=true], [tiesMethod]='latest')cumsumTopN, cumavgTopN, cumstdTopN, cumstdpTopN, cumvarTopN, cumvarpTopN, cumskewTopN, cumkurtosisTopN
cumTopN( X, Y, S, top, [ascending=true], [tiesMethod='latest'])cumbetaTopN, cumcorrTopN, cumcovarTopN, cumcovarpTopN, cumwsumTopN
Windowing Logic
The function stably sorts X (or X, Y) by S in the order specified by ascending, then obtains the first top elements for calculation in a cumulative window.
The following example illustrates the calculation rules:
X = [2, 1, 5, 3, 4, 3, 1, 9, 0, 5, 2, 3]
S = [5, 8, 1, 9, 7, 3, 1, NULL, 0, 8, 7, 7]
cumsumTopN(X, S, top=3)
// output: [2,3,8,8,11,10,9,9,6,6,6,6]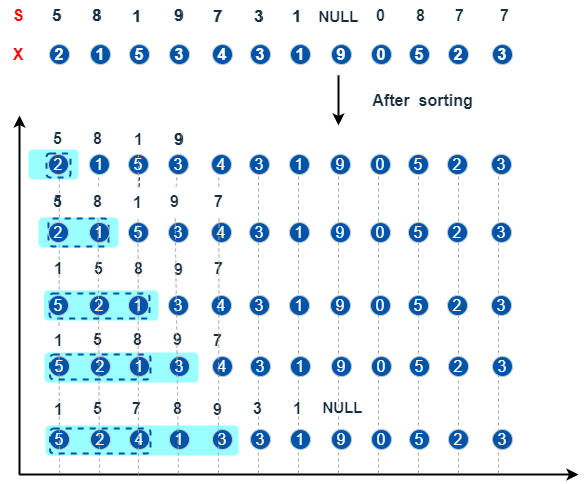
The following examples show the usage of parameter tiesMethod:
X = [2, 1, 4, 3, 4, 3, 1]
S = [5, 8, 1, 1, 1, 3, 1]
// For the last cumulative window, there are four elements of value 1
// As tiesMethod is not specified, the default 'latest' is used, meaning the latest 3 occurrences of 1 (corresponding to 3, 4, 1 of X) are selected
cumsumTopN(X, S, top=3)
// output: [2,3,7,9,11,11,8]
// As tiesMethod is set to 'oldest', the first 3 occurrences of 1 (corresponding to 4, 3, 4 of X) are selected
cumsumTopN(X, S, top=3, tiesMethod=`oldest)
// output: [2,3,7,9,11,11,11]
// As tiesMethod is set to 'all', all the occurrences of 1 (corresponding to 4, 3, 4, 1 of X) are selected
cumsumTopN(X, S, top=3, tiesMethod=`all)
// output: [2,3,7,9,11,11,12]